All processing stages
Agricultural Activity
Every contemporary society and the different forms of aggregation in which it is manifested have the duty to operate respecting the interests of future generations. Agricultural enterprises can not be exempt from this approach in the exercise of their activity; indeed being strictly related to the environment, they must take care of all three aspects that the evolution of the debate has now decreed as the cornerstones of the sustainable development of each business: environment, social security and economic growth.
Our company, strengthened by these principles, aiming to maintain the economic, environmental and social security sustainability standards achieved.
1st Phase
Ground preparation
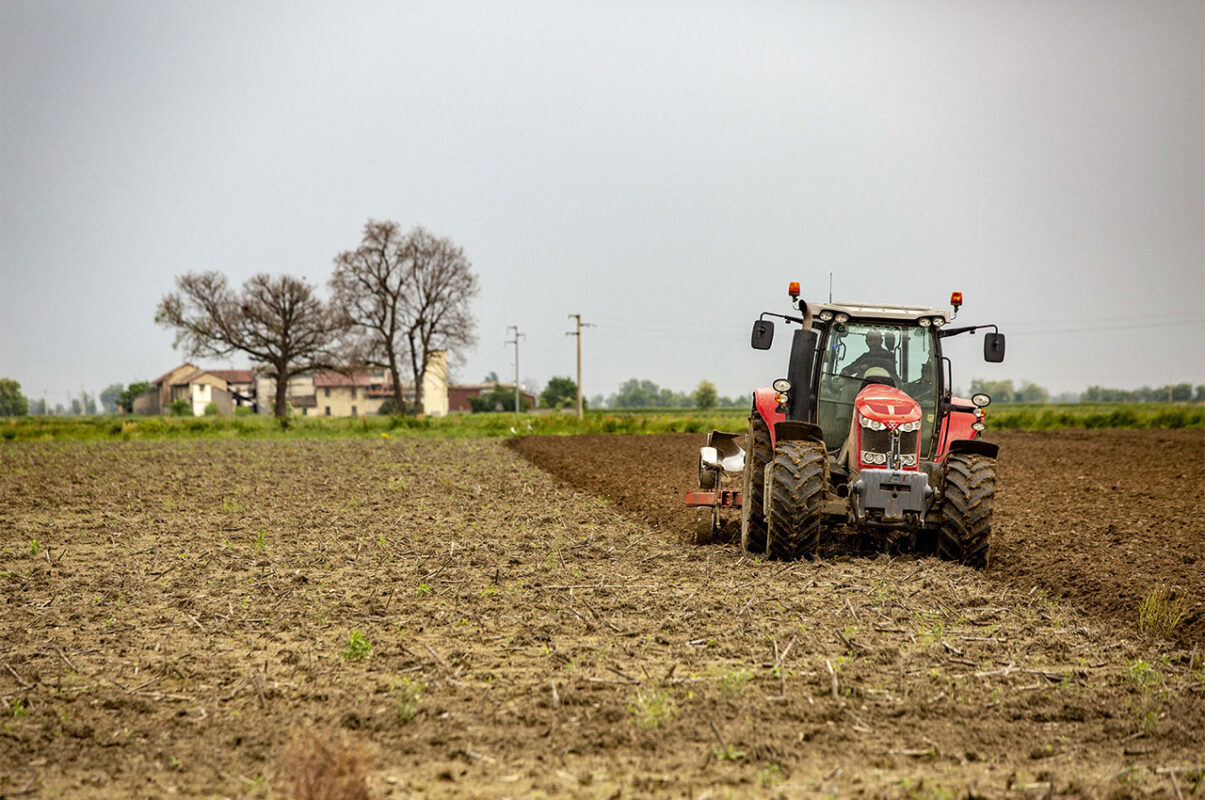
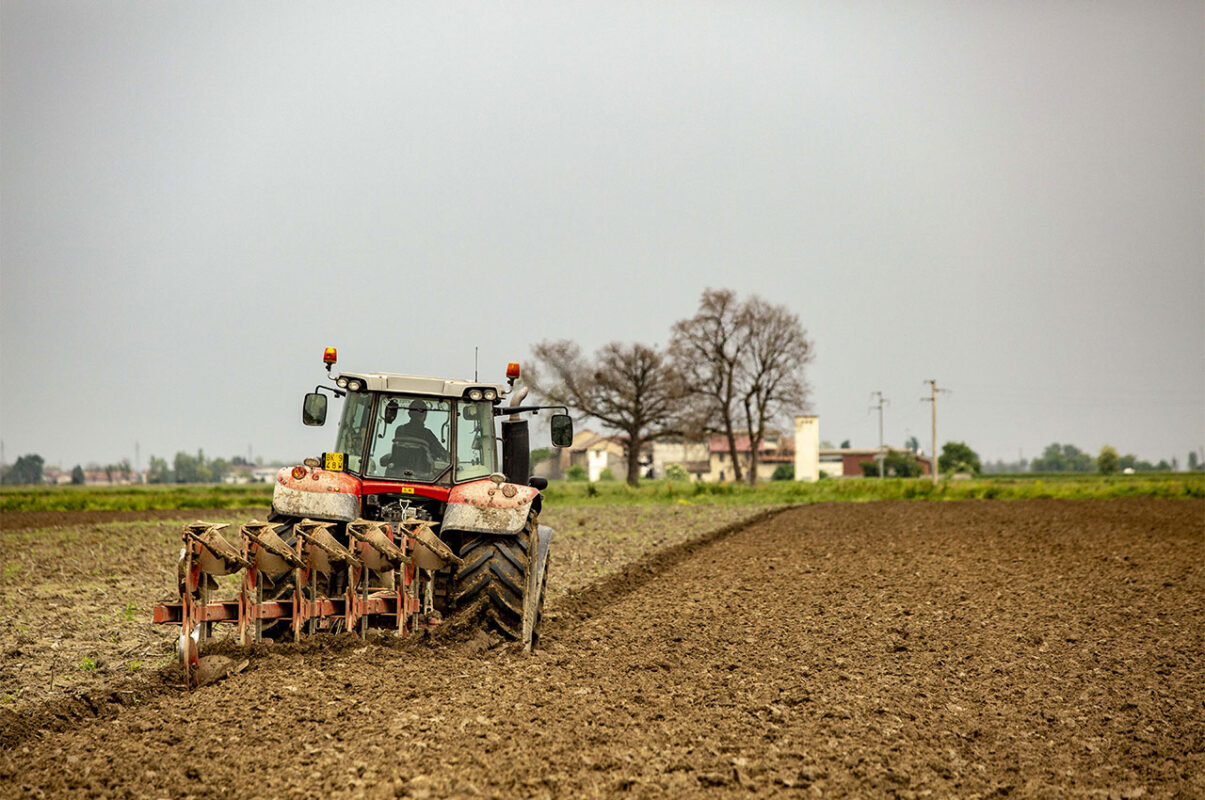
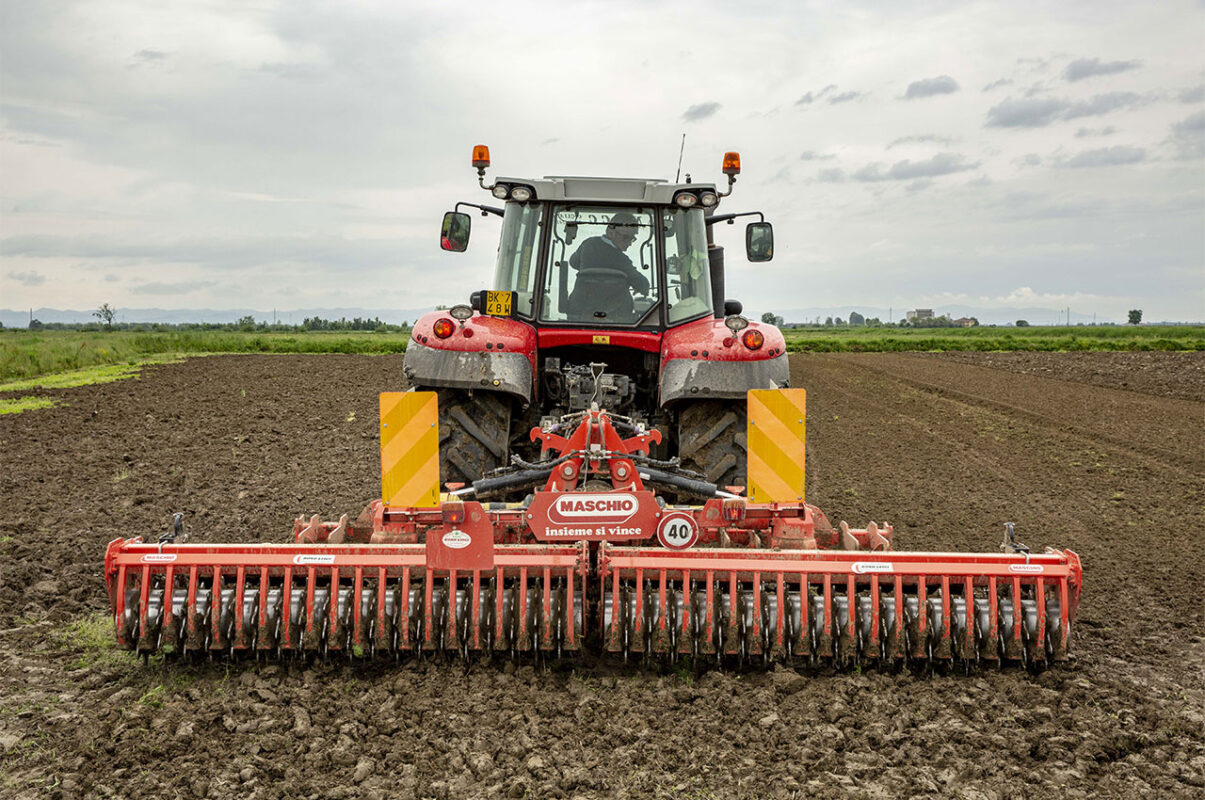
The first operations are aimed at preparing the ground for sowing. In addition to the usual maintenance of banks and ditches, this phase mainly involves ploughing.
The purpose is to aerate and favor the burial of the previous crop and take advantage of the winter frost to make the clay soils easier to work in the spring, as well as having more time for the microbial degradation of organic residues.
Soil refinement is then finalized by harrowing to prepare the next sowing.
2rd Phase
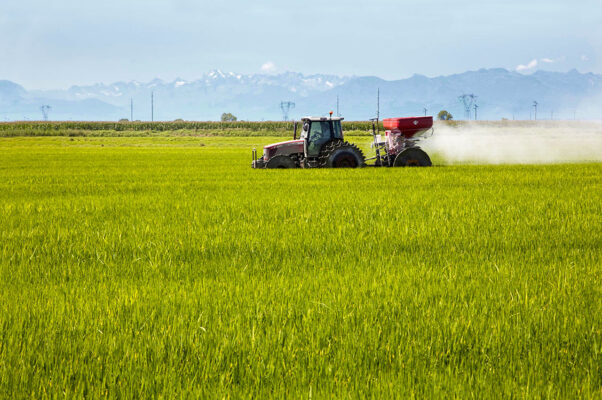
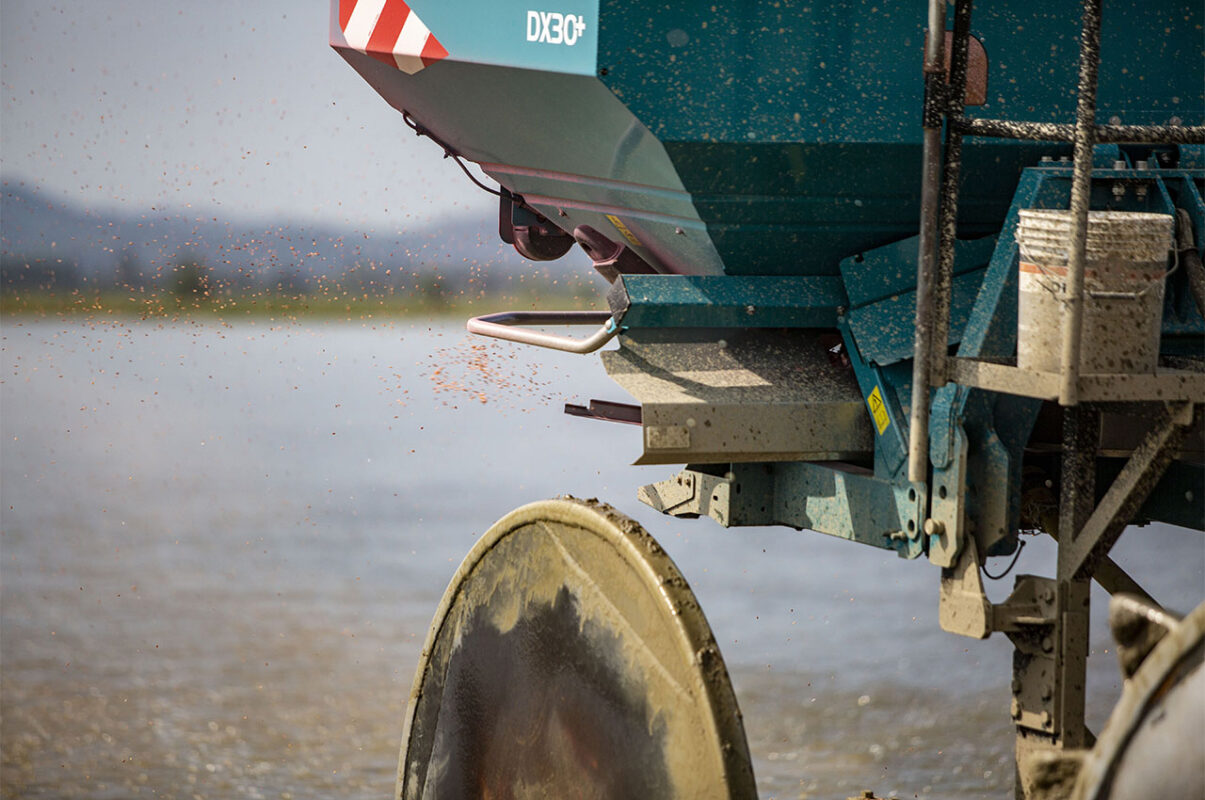
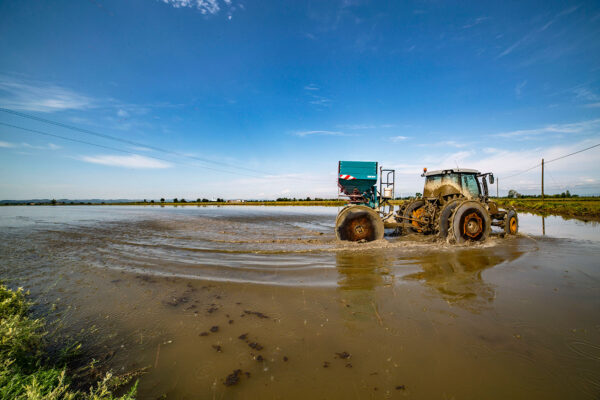
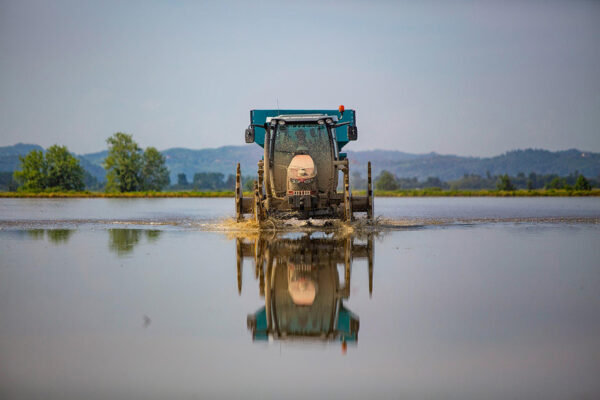
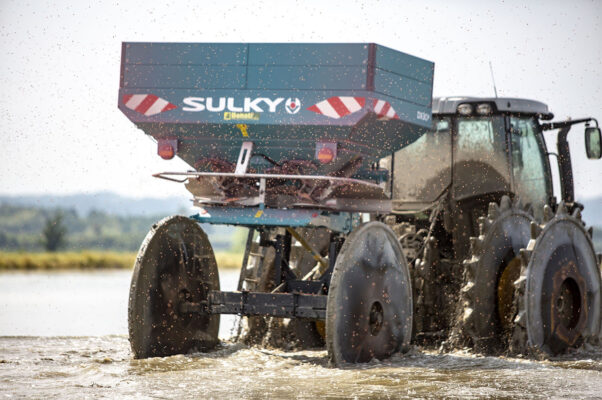
Fertilization
The purpose of fertilization is to basically provide the plant with the proper amount of nutrients, that might not always be available in the ground.
Through the use of precision technical equipment, balanced growth of the crops is ensured. By providing the right quantity of fertilizers, the optimization of production is guaranteed, preserving at the same time the right organoleptic conditions of each variety.
3nd Phase
Sowing
This operation, which can be carried out on either submerged or dry soil, is performed from April onwards, taking into account the characteristics of the soil and the variety of rice.
4th Phase
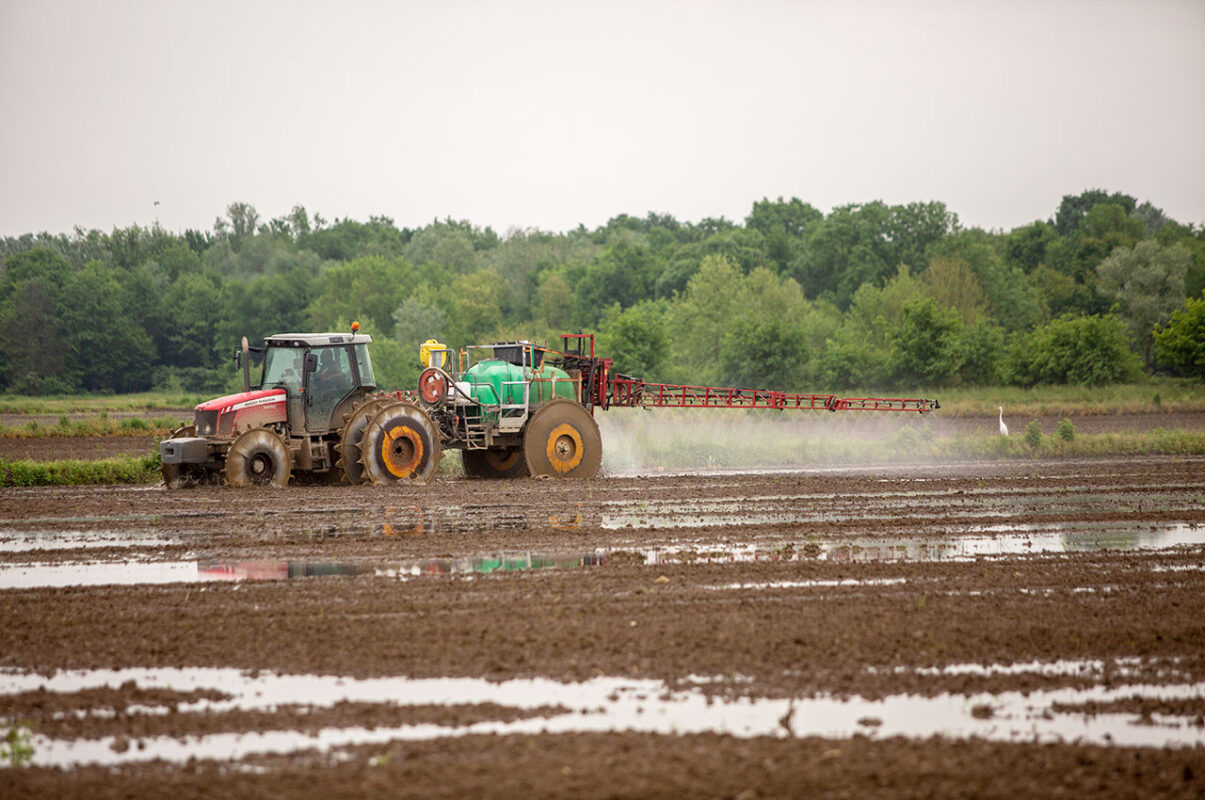
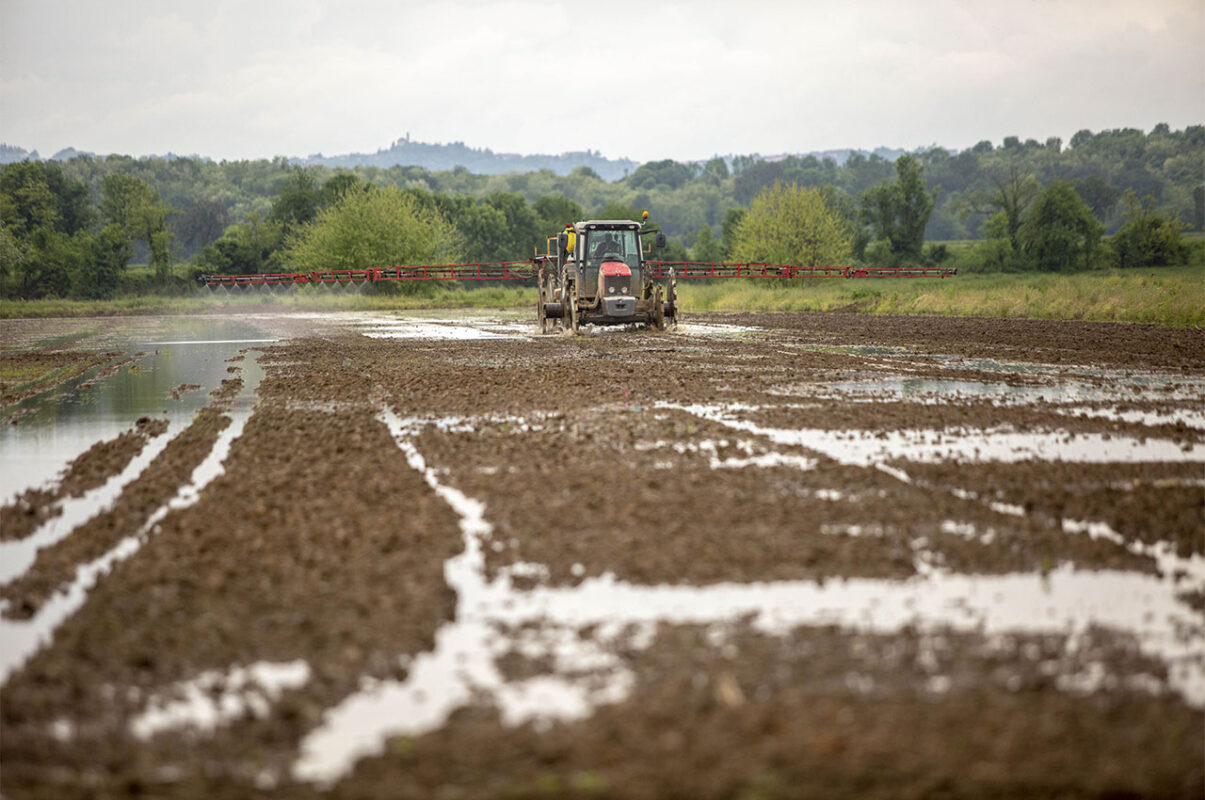
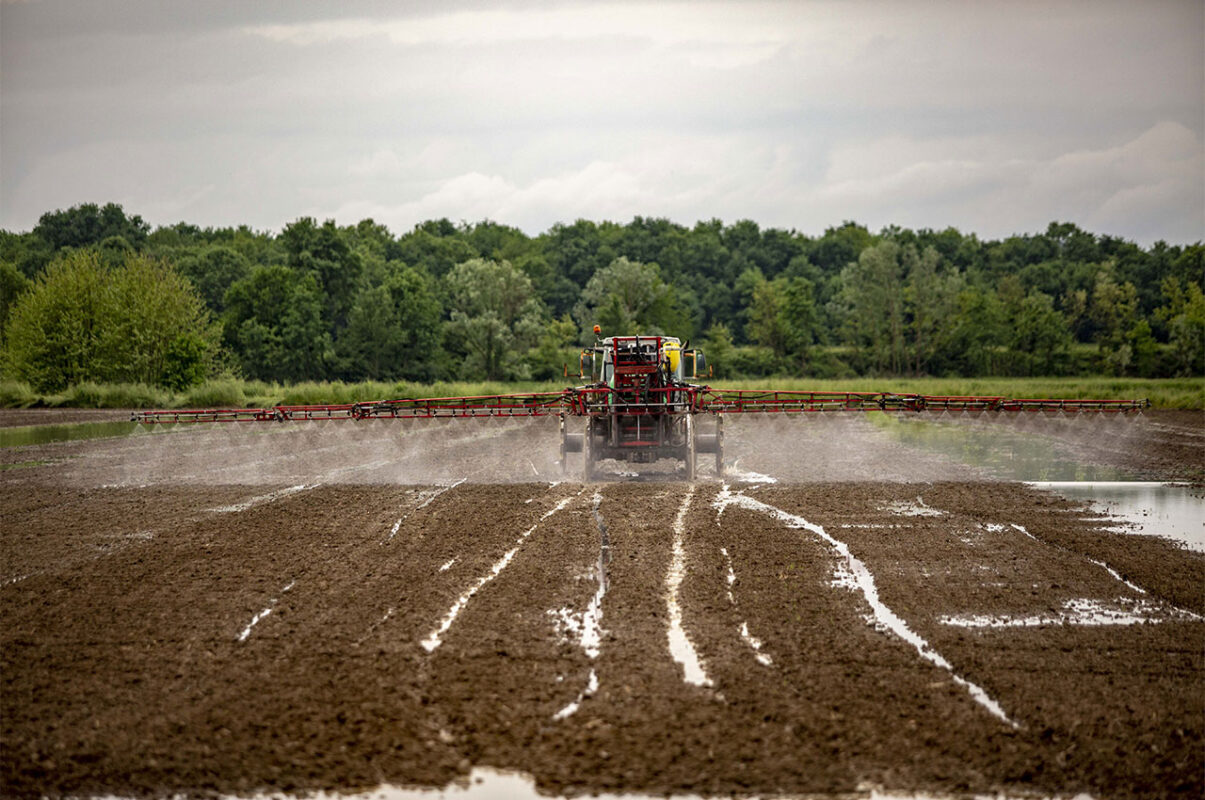
Phytosanitary treatment
Managing infesting plants is a key aspect of rice cultivation.
The fight against weeds is carried out through a combined action of different means such as agronomic, mechanical, physical and chemical methods with the purpose of obtaining an environment as clean as possible before harvesting.
5th Phase
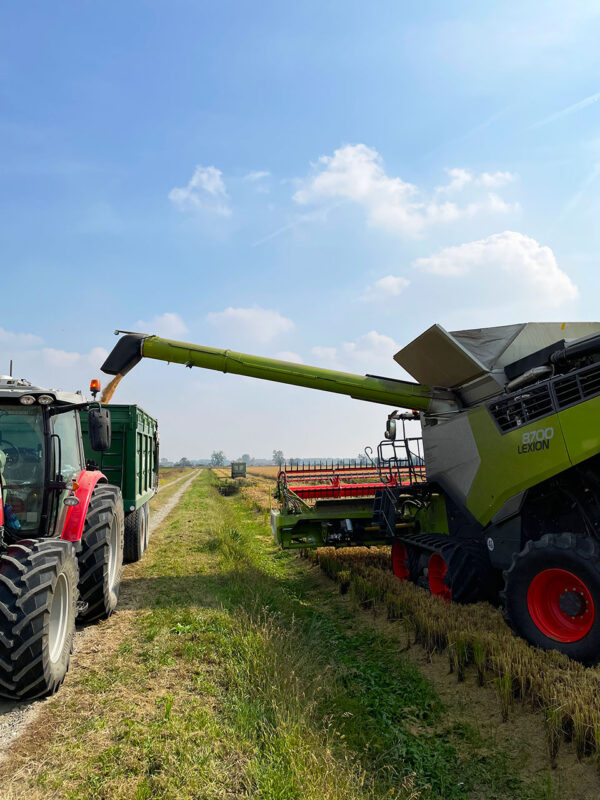
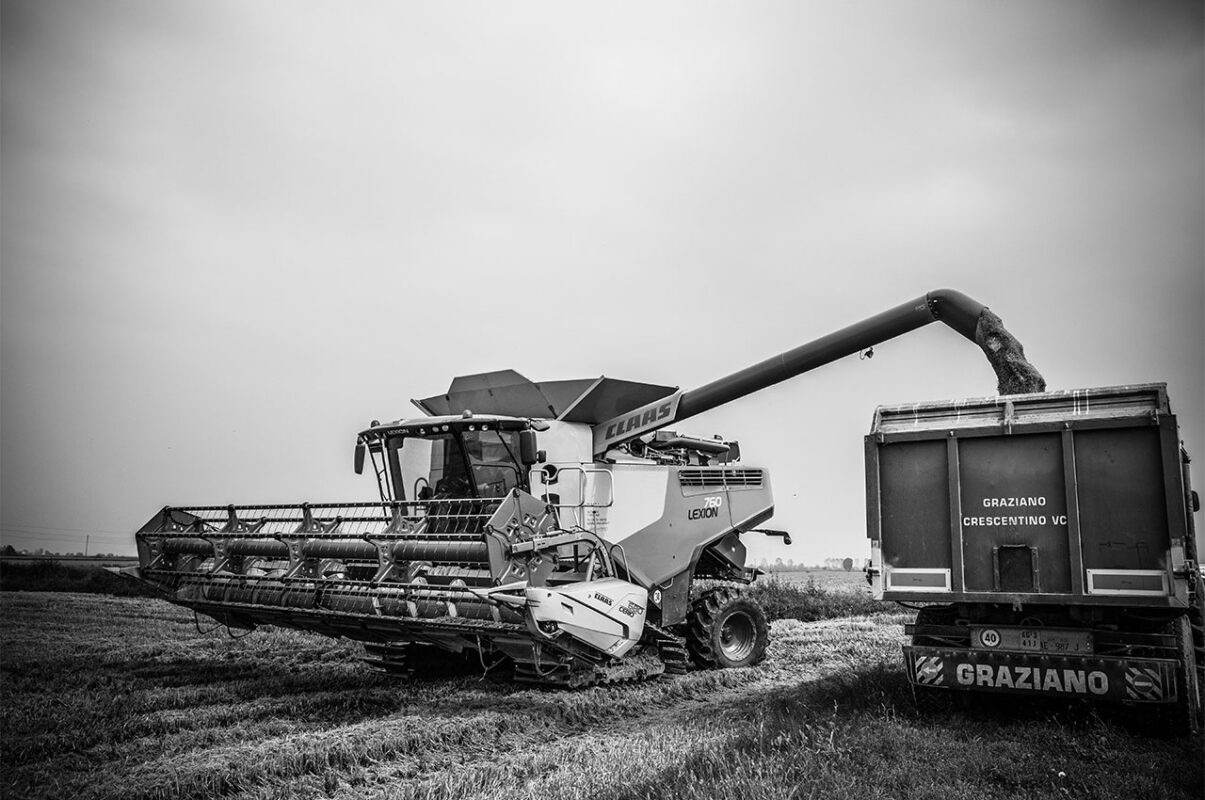
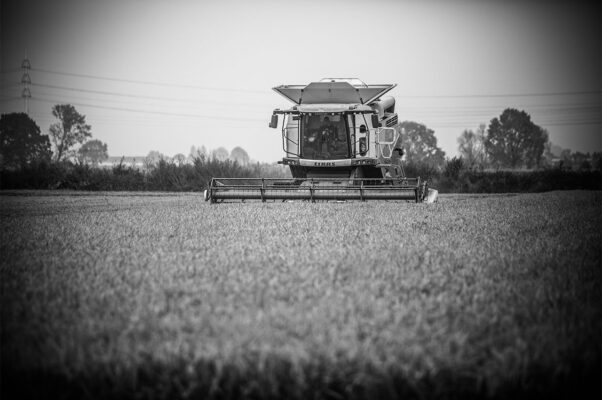
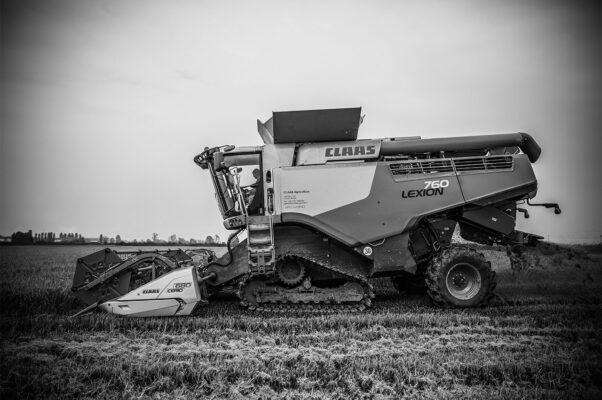
Harvesting
Rice sown in spring starts its ripening phase in mid/end of August and, once it has reached the right stage, it can be harvested on dry soil between September and the whole month of October.
6th Phase
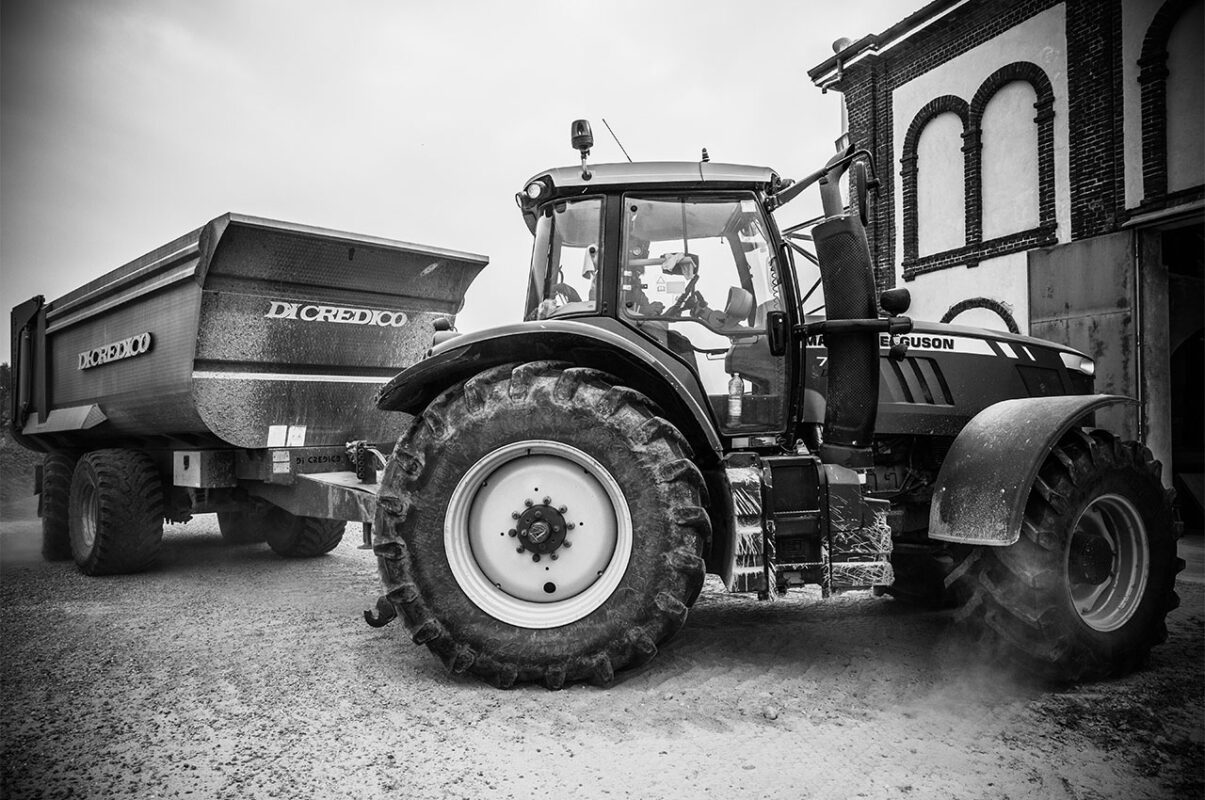
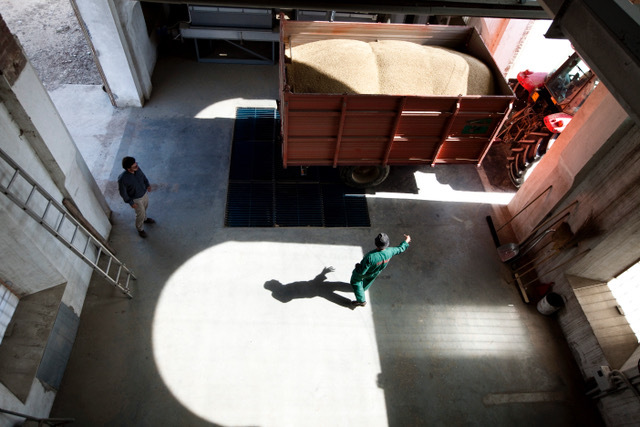
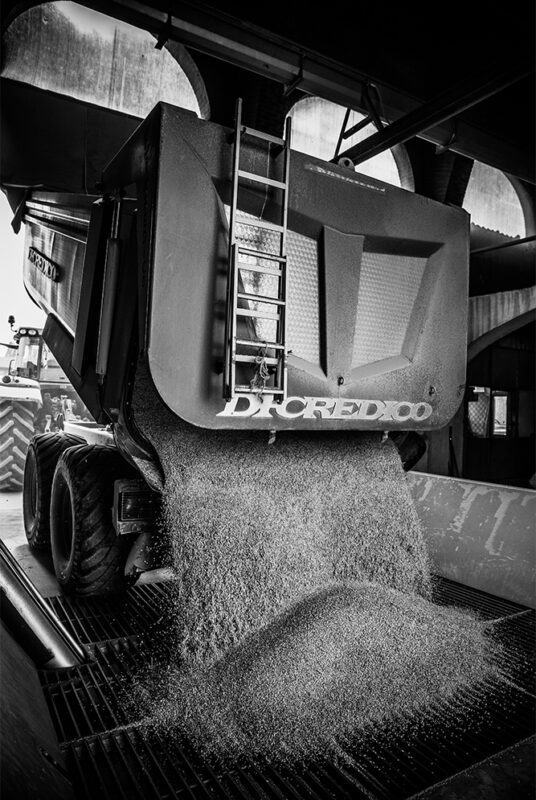
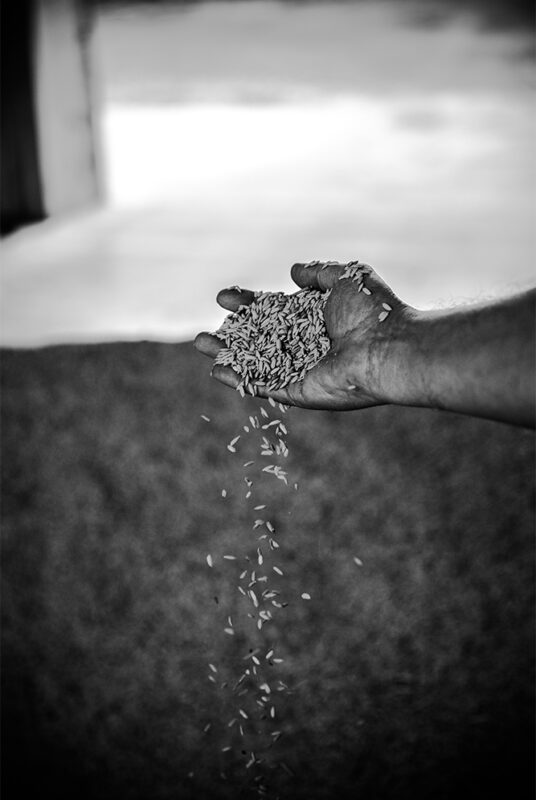
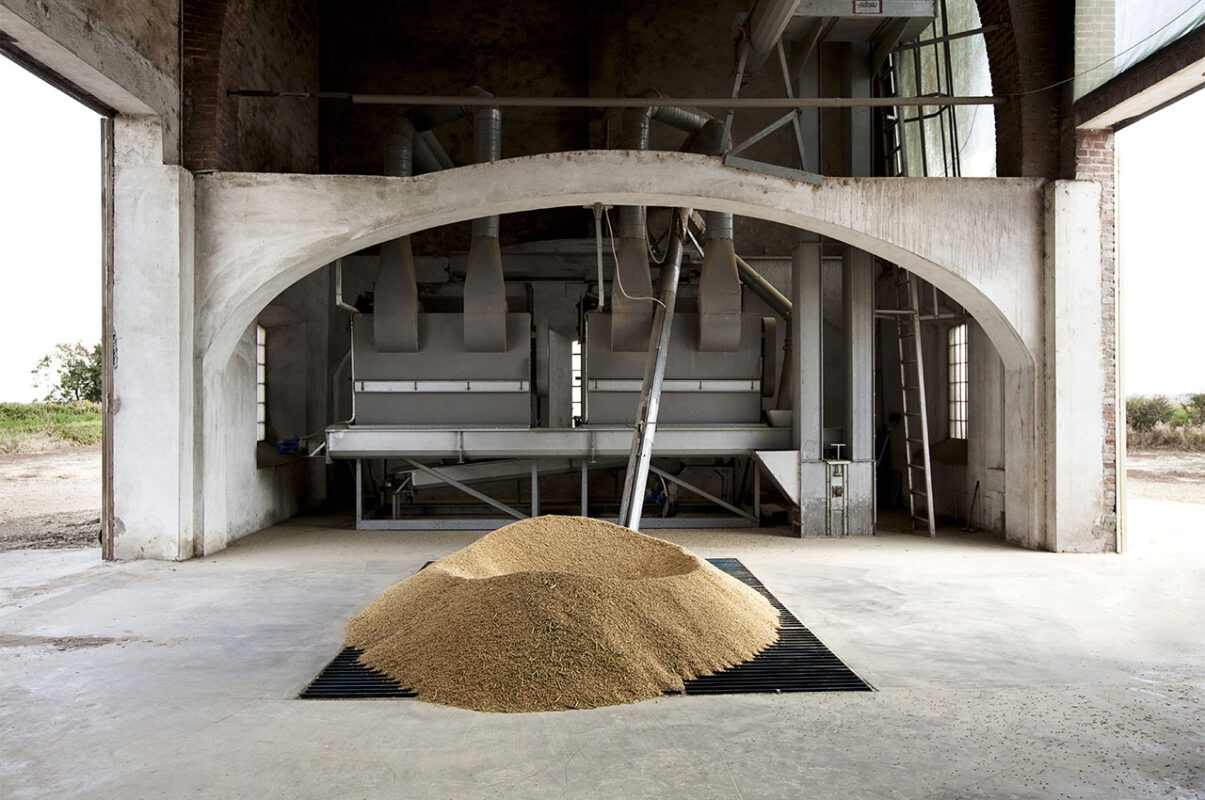
Drying and storage
Harvested paddy rice is rapidly put to the dry to avoid the degradation process of the grain.
This process is carried out with particular care and gradually, in order to maintain the integrity of the grain.
Once dried, the rice is transferred to silos for correct storage and ready for the next processing operations.

 Italiano
Italiano




























